Discover Effective Risk Management Strategies in ISO 9001

Strengthening Risk Management with ISO 9001 Certification
Modern organizations face escalating quality and operational risks that erode profitability and reputation. ISO 9001 certification embeds systematic risk management strategies in ISO 9001 through a proactive framework that identifies, analyzes, evaluates, and treats uncertainties before they become threats. This article explains what risk-based thinking means, outlines the ISO 9001 risk assessment process, highlights certification benefits, shows integration with other standards, and presents best practices—including tool selection and internal audits—to strengthen resilience and decision-making.
What Is ISO 9001 Risk-Based Thinking and Why Is It Important?
Risk-based thinking in ISO 9001:2015 mandates that an organization embed risk and opportunity considerations into every process, promoting consistent quality outcomes and preventing defects. By shifting from reactive fire-fighting to proactive planning, risk-based thinking enhances process stability, reduces waste, and aligns quality objectives with strategic goals.
Ideagen, ISO 9001:2015 revision explained: Risk-based thinking, (2024)
Risk-Based Thinking in ISO 9001:2015
The 2015 revision of ISO 9001 replaced “preventive action” with a “risk-based approach,” which encourages organizations to integrate risk considerations into their management systems for improved customer satisfaction and consistent quality of goods and services.
This principle paves the way to compare traditional risk management and to explore the standard’s core principles in depth.
How Does Risk-Based Thinking Differ from Traditional Risk Management?
Risk-based thinking integrates risk evaluation into the quality management system rather than treating it as a standalone activity. Traditional risk management often operates in silos—typically within safety or finance—whereas ISO 9001 embeds risk assessment in planning, operations, and performance evaluation. This holistic approach ensures that every process owner considers uncertainty alongside targets and resources.
What Are the Core Principles of ISO 9001 Risk-Based Thinking?
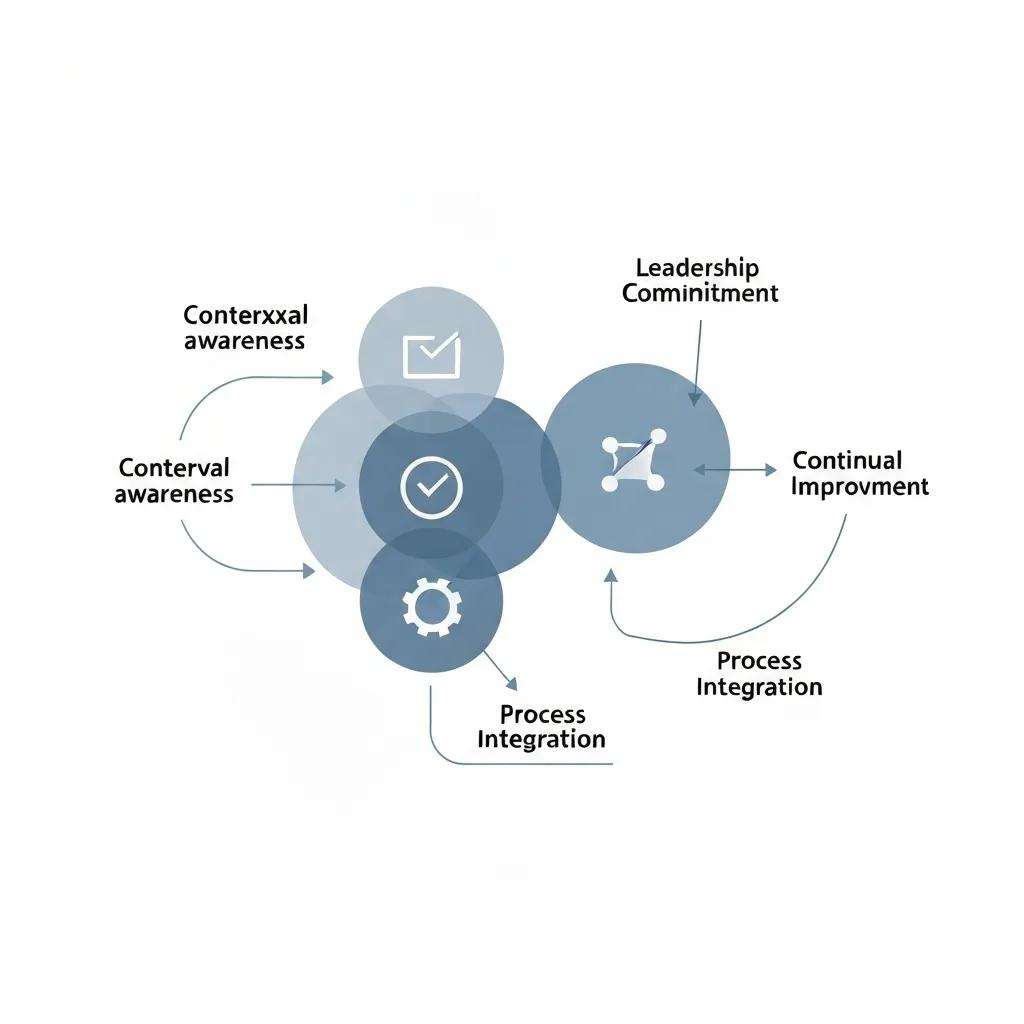
Below are the foundational principles that empower proactive risk management:
- Contextual Awareness – Understanding internal and external factors that influence quality goals.
- Leadership Commitment – Top management ensures resources and culture support risk identification.
- Process Integration – Embedding risk assessment and control into operational workflows.
- Continual Improvement – Monitoring risk treatment effectiveness and refining actions.
These principles set the stage for a structured risk assessment process.
How Does the ISO 9001 Risk Assessment Process Work?
ISO 9001 outlines a five-phase risk assessment process that guides organizations through systematic uncertainty management to protect quality objectives and compliance.
What Are the Steps in ISO 9001 Risk Identification and Analysis?
Before controls are applied, organizations must:
- Gather context data from stakeholders, regulators, and market trends.
- Use tools such as FMEA or SWOT to list potential failures and opportunities.
- Analyze each risk’s likelihood and consequence on process performance.
This structured identification and analysis enable informed prioritization of risks.
How Is Risk Evaluation and Treatment Implemented in ISO 9001?
Once risks are assessed, organizations evaluate significance and determine treatment:
- Risk Evaluation – Compare risk scores against criteria to decide on action.
- Risk Treatment – Select avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance strategies.
- Control Implementation – Define responsibilities, resources, and timelines for risk controls.
- Monitoring – Track key indicators to verify treatment effectiveness.
By closing the loop, ISO 9001 ensures that controls remain effective and aligned with quality goals.
What Are the Benefits of ISO 9001 Certification for Risk Management?
ISO 9001 certification delivers a structured risk management framework that improves decision-making, strengthens resilience, and builds stakeholder confidence by embedding risk consideration into quality processes.
British Assessment Bureau, Benefits of ISO 9001 Certification, (2024)
Benefits of ISO 9001 Certification for Risk Management
ISO 9001 certification provides a structured risk management framework that enhances decision-making, strengthens resilience, and builds stakeholder confidence by embedding risk consideration into quality processes.
How Does ISO 9001 Improve Organizational Resilience and Decision-Making?
Certification mandates a culture of risk awareness: process owners routinely review performance metrics, adapt controls, and make data-driven decisions. This resilience reduces downtime, accelerates corrective actions, and aligns objectives with evolving market conditions.
How Does Certification Increase Stakeholder Confidence and Compliance?
Earning ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality and risk reduction, reassuring customers, regulators, and investors. Certified organizations report fewer nonconformities and stronger compliance with contractual and regulatory requirements, enhancing reputation and trust.
How Does ISO 9001 Integrate with Enterprise Risk Management and Other Standards?

ISO 9001 is designed to work in tandem with broader risk frameworks and related ISO standards, creating a unified governance model.
What Is the Relationship Between ISO 9001 and ISO 31000 Risk Management?
| Standard | Focus Area | Integration Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System | Embeds risk-based planning in daily processes |
| ISO 31000 | Risk Management Principles | Provides guidelines for risk framework design |
| Combined | Quality + Enterprise Risk | Ensures consistent criteria and shared terminology |
Extrend Consulting, ISO 31000: why integrate this standard?, (2023)
ISO 9001 and ISO 31000 Alignment
ISO 9001 integrates risk-based planning into daily processes, while ISO 31000 provides guidelines for risk framework design, ensuring consistent criteria and shared terminology.
How Does ISO 9001 Align with ISO 27001 and Other Related Standards?
ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 share a common PDCA cycle. While ISO 9001 emphasizes product and service quality, ISO 27001 focuses on information security controls. Organizations can integrate both by mapping risk assessment outputs and controls, leveraging unified documentation and audit processes to optimize resource use and compliance.
What Are the Best Practices for Implementing Risk Management Under ISO 9001?
Effective implementation relies on consistent monitoring, specialized tools, and rigorous verification to embed risk awareness and continuous improvement across the organization.
How Can Organizations Use Tools and Software to Support ISO 9001 Risk Management?
Selecting dedicated QMS software enhances visibility and collaboration:
- Implement risk registers with automated reminders for reviews.
- Use FMEA modules to score and track failure modes over time.
- Deploy dashboards for real-time monitoring of risk indicators.
Organizations should also budget appropriately for these solutions; understanding the ISO 9001 certification cost helps align technology investment with overall implementation planning.
What Role Do Internal Audits Play in Verifying ISO 9001 Risk Management Effectiveness?
Internal audits verify that risk controls function as intended by reviewing documented procedures, interviewing process owners, and testing control activities. Auditors identify gaps, recommend enhancements, and confirm that corrective actions drive continual improvement—closing the loop on ISO 9001’s risk-based framework.
ISO 9001 certification transforms risk management from a reactive discipline into a strategic advantage, driving consistent quality, resilience, and stakeholder trust. By adopting risk-based thinking, following a structured assessment process, integrating with other standards, and applying best practices—supported by tools and rigorous audits—organizations lay the foundation for sustainable performance and competitive differentiation. For tailored guidance on implementing these strategies, explore ISO 9001 consulting services or request a demo of leading QMS software solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of organizations can benefit from ISO 9001 certification?
ISO 9001 certification is applicable to organizations of all sizes and sectors, including manufacturing, services, healthcare, and education. Any organization aiming to improve its quality management processes and enhance customer satisfaction can benefit from this certification. It provides a framework for consistent quality improvement, which is essential for businesses looking to gain a competitive edge and build trust with stakeholders. Additionally, organizations seeking to comply with regulatory requirements or improve operational efficiency will find ISO 9001 particularly advantageous.
How long does it take to achieve ISO 9001 certification?
The time required to achieve ISO 9001 certification varies based on the organization’s size, complexity, and existing quality management practices. Generally, the process can take anywhere from a few months to over a year. Key factors influencing the timeline include the readiness of the organization, the thoroughness of the documentation, and the effectiveness of training programs for staff. Organizations that are well-prepared and have existing quality management systems in place may achieve certification more quickly than those starting from scratch.
What are the costs associated with obtaining ISO 9001 certification?
The costs of obtaining ISO 9001 certification can vary widely depending on several factors, including the size of the organization, the complexity of its processes, and the certification body chosen. Typical expenses include training costs, consultancy fees, internal resource allocation, and the certification audit itself. Organizations should also consider ongoing costs for maintaining compliance, such as internal audits and continuous improvement initiatives. Budgeting for these costs is crucial to ensure a successful certification journey and long-term sustainability.
How often do organizations need to renew their ISO 9001 certification?
ISO 9001 certification is typically valid for three years. However, organizations must undergo regular surveillance audits, usually annually, to ensure ongoing compliance with the standard. These audits help verify that the organization continues to meet ISO 9001 requirements and is committed to continuous improvement. After the three-year period, organizations must complete a recertification audit to maintain their certification status. This cycle encourages organizations to consistently uphold quality management practices and adapt to any changes in their operational environment.
What role does employee training play in ISO 9001 implementation?
Employee training is a critical component of successful ISO 9001 implementation. It ensures that all staff members understand the quality management system, their roles within it, and the importance of risk-based thinking. Training helps foster a culture of quality and continuous improvement, empowering employees to identify risks and contribute to process enhancements. Organizations should invest in regular training sessions and workshops to keep employees informed about updates to the standard and best practices, ultimately leading to better compliance and performance outcomes.
Can ISO 9001 certification help with international business operations?
Yes, ISO 9001 certification can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to operate internationally. It demonstrates a commitment to quality management and customer satisfaction, which are crucial for gaining trust in global markets. Many international clients and partners prefer or require ISO 9001 certification as a condition for doing business. Additionally, the standard’s emphasis on risk management and continuous improvement aligns well with the complexities of international operations, helping organizations navigate challenges and maintain consistent quality across borders.
Conclusion
ISO 9001 certification revolutionizes risk management by embedding proactive strategies that enhance decision-making and bolster organizational resilience. This structured approach not only fosters stakeholder confidence but also aligns quality objectives with strategic goals, ensuring sustainable performance. By embracing risk-based thinking and implementing best practices, organizations can transform potential threats into opportunities for growth. Discover how our ISO 9001 consulting services can guide you in achieving these benefits today.

